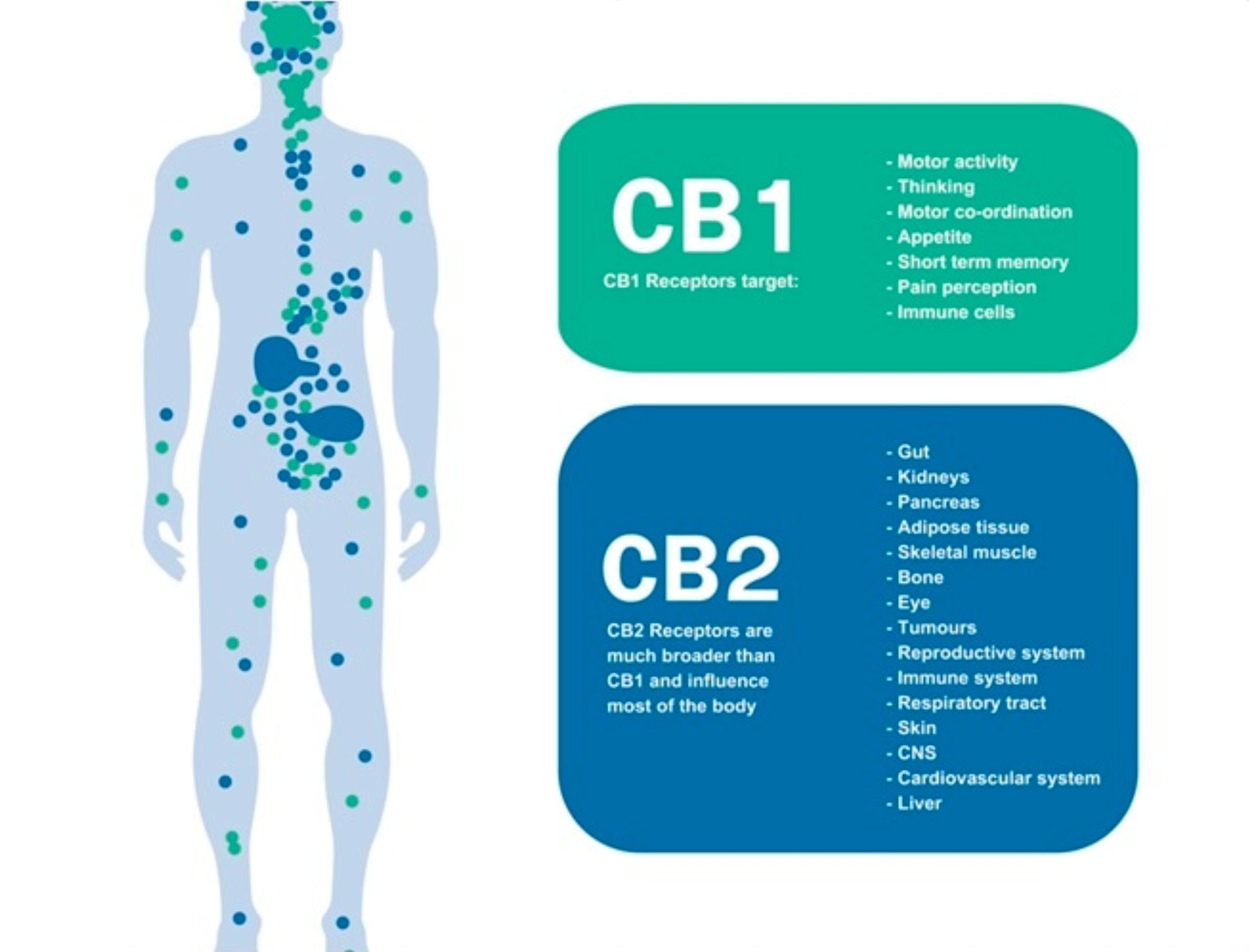
Endocannabinoid System: CB1 & CB2 receptors.
First things first…why should you care about the Endocannabinoid (ECS) System?
Sometimes we feel a bit off, but we’re not sure why. We feel stressed, tired, anxious, achy, and have trouble sleeping. It could be that our ECS is off too, and not doing its job regulating various systems that regulate all of this for us. The ECS is essential to us feeling well, and mysterious too. Got your attention yet?
Simple Definition of ECS
The Endocannabinoid (ECS) System regulates and controls many of our most critical bodily functions, such as learning and memory, emotional processing, sleep, temperature control, pain control, inflammatory and immune responses, and eating. Think of the ECS as the master regulator of the body’s other systems. The ECS is designed to help maintain homeostasis, a balance of processes in our system, keeping our systems running smoothly.
//ho-me-o-sta-sis// - the tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements, primarily maintained by physiological processes.
CBD can help your body to maintain homeostasis, improve sleep, and reduce aches, pains and inflammation. Yellow Athletic's All Star Products with ultra high potency CBD, specifically for athletes and athletic recovery, are designed to tune up your Endocannabinoid System. Many athletes in the NFL, MLB and Olympics have turned to CBD, why shouldn’t you?
Expanded Definition of ECS
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a group of receptors and chemicals found throughout the body, including in the brain, organs, connective tissues, and immune cells. The ECS plays a role in regulating a variety of physiological processes, including appetite, pain sensation, mood, and sleep. The ECS comprises two main types of receptors: CB1 receptors, mainly found in the brain and nervous system, and CB2 receptors, mostly in the immune system. The two main endocannabinoids, which are made by the body, are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These endocannabinoids bind to the receptors in the ECS and help to regulate various physiological processes. Additionally, compounds called phytocannabinoids, can also bind to these receptors and have similar effects.

If you’re curious about the ECS and its relationship with CBD, visit Yellow Athletic to learn more such as: Ways CBD can enhance your fitness regime, Major Benefits of CBD for Athletes, Reasons athletes are flocking to CBD, What kind of CBD is best for athletes…and more.
For more in depth information:
The following content is from Harvard Medical School’s "The Endocannabinoid System: Essential and Mysterious" August 11, 2021
Many of us have heard of some of the transmitter systems within our bodies, such as the sympathetic nervous system, which gives us our fight-or-flight response. Fewer have heard of the more recently discovered endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is amazing when you consider that the ECS is critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning. The ECS regulates and controls many of our most critical bodily functions such as learning and memory, emotional processing, sleep, temperature control, pain control, inflammatory and immune responses, and eating. The ECS is currently at the center of renewed international research and drug development.
What is the ECS?
The ECS comprises a vast network of chemical signals and cellular receptors that are densely packed throughout our brains and bodies. The "cannabinoid" receptors in the brain — the CB1 receptors — outnumber many other receptor types on the brain. They act like traffic cops to control the levels and activity of most of the other neurotransmitters. This is how they regulate things: by immediate feedback, turning up or down the activity of whichever system needs to be adjusted, whether hunger, temperature, or alertness.
To stimulate these receptors, our bodies produce molecules called endocannabinoids, which have a structural similarity to molecules in the cannabis plant. The first endocannabinoid discovered was named anandamide after the Sanskrit word ananda for bliss. All of us have tiny cannabis-like molecules floating around in our brains. The cannabis plant, which humans have been using for about 5,000 years, essentially works its effect by hijacking this ancient cellular machinery.
A second type of cannabinoid receptor, the CB2 receptor, exists primarily in our immune tissues and is critical to helping control our immune functioning. It plays a role in modulating intestinal inflammation, contraction, and pain in inflammatory bowel conditions. CB2 receptors are particularly exciting targets of drug development because they don’t cause the high associated with cannabis that stimulating the CB1 receptors does (which is often an unwanted side effect).
The ECS's role in learning and memory
We know that the ECS plays a critical role in learning and memory due to several lines of research. The most obvious observation is that one of the main side effects of high dosages of recreational cannabis use is the temporary disruption of short-term memory. Memory returns to normal with abstinence. There have also been some sophisticated studies of how humans acutely respond to the administration of THC (the active ingredient in cannabis) and how it alters both their ability to memorize things in the short term and the patterns observed on their functional brain imaging.
According to the popular writer Michael Pollan in his bestselling book The Botany of Desire, cannabis is one of the plants humans have cultivated or co-evolved with for thousands of years. This is in part, Pollan writes, because the act of forgetting plays a valuable role in the ability of our brains to function without being overloaded with data from our senses that we are continually bombarded with. Pollan hypothesizes that if we didn’t forget, we wouldn’t function, and cannabis helps us do this. The role that the ECS plays in forgetting also opens up opportunities for the treatment of PTSD, a condition in which there are unpleasant, intrusive memories that people can’t help but remember, and that cause a whole syndrome of troublesome and dangerous symptoms related to the pathological remembering.
The ECS's role in hunger and fine-tuning weight-loss medications
The cautionary tale of the drug rimonabant, a drug that blocks the CB1 receptor, is an interesting example of the central role the ECS plays in so many crucial functions. It was developed as an anti-obesity drug. The thinking was that the ECS controls hunger. We know this because, among other lines of evidence, cannabis gives you "the munchies," so if you block the CB1 receptor it should cause weight loss. Rimonabant did cause weight loss, quite successfully. But, because the ECS also regulates mood, it had to be withdrawn from the market on an emergency basis because people who were taking it were becoming suicidal. However, we can imagine a case, as we better understand the complexities of the ECS, where we may be able to create a weight-loss medication that acts on those cannabinoid receptors that affect weight loss, but that doesn’t act on those receptors that control mood.
Exploration of the ECS may lead to new drug discoveries
If your Endocannabinoid System is not at its best, and you have aches, pains, inflammation or trouble sleeping, visit Yellow Athletic to find products to alleviate what ails you.
Learn More:
The Endocannabinoid System: Essential & Mysterious" Harvard Medical School 2021
National Library of Medicine Article on ECS
National Library of Health Article on the ECS and Energy Regulation



 Study of the ECS was initially focused on attempts to understand (and demonize) an illegal drug, but new research has since flourished into a far more broad-based exploration into what is an astoundingly intricate and far-reaching system by which our bodies learn, feel, motivate, and keep themselves in balance. We are truly at the dawn of an age of discovery of the ECS and the development of new medicines that may help alleviate some of the cruelest diseases that people (and animals) suffer from. I am incredibly excited to see what discoveries await us as we continue to untangle the mysteries of the ECS.
Study of the ECS was initially focused on attempts to understand (and demonize) an illegal drug, but new research has since flourished into a far more broad-based exploration into what is an astoundingly intricate and far-reaching system by which our bodies learn, feel, motivate, and keep themselves in balance. We are truly at the dawn of an age of discovery of the ECS and the development of new medicines that may help alleviate some of the cruelest diseases that people (and animals) suffer from. I am incredibly excited to see what discoveries await us as we continue to untangle the mysteries of the ECS.